.png)
Co-location Analysis
| Data | |
|---|---|
| Suggested tools | Geoda |
| Category | Spatial Analysis |
| Variable | BivariableMultivariable |
refer to Spatial Autocorrelation for a general reference card about spatial autocorrelation.
Overview
Colocation analysis is a spatial analysis method used to identify the geographical co-occurrence of two or more types of features within a given spatial context. This method is particularly useful in urban health and wellbeing studies to understand how different urban elements (such as healthcare facilities, parks, pollution sources, etc.) are spatially related to each other and to the populations they serve or affect. Here, we refer to the co-Location Join Count of spatial features instead of colocation quotient statistic for points.
Implication on urban health
Targeted Public Health Interventions
Quantile LISA can identify spatial clusters of high-risk areas where certain health outcomes and determinants co-locate. For example, if a cluster is identified where high pollution levels co-locate with high rates of respiratory diseases, targeted interventions can be designed to address both the environmental and health issues simultaneously. This precision in identifying and addressing health issues can lead to more effective public health strategies and better health outcomes.
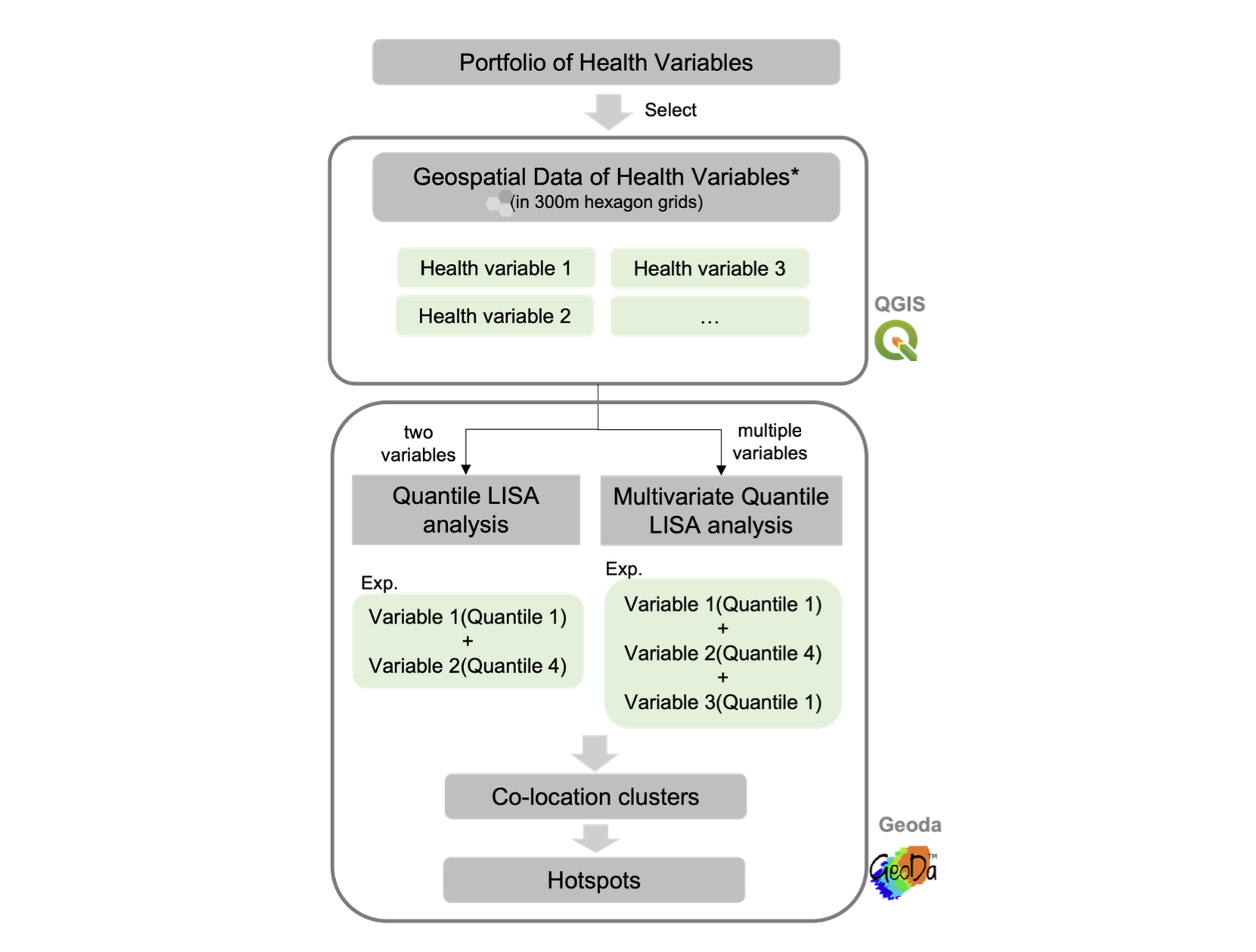
Technique — Quantile LISA
Quantile LISA is a local spatial autocorrelation statistic with bivariate or
multivariate discrete variables, serving as an alternative to Multivariate local Geary20.
The analysis takes quantiles of variables (two or multiple variables) as
input data and
searches for co-location clusters. The
output of this analysis is a map representation of
the significance of the spatial co-location between two or multiple variables, including
significant levels.
Tutorial
We implement the analysis in open-sourced geoprocessing on Geoda 1.20 Version. The spatial weight used in the analysis is the queen continuity. The two steps are shown below:
- Select a pair of variables (one from health outcome and the other are health determinates) and import them into Geoda;
- In the menu toolbar, activate Space->Quantile LISA variables function;
- For each variable, set the number of quantiles and choose the quantile (e.g.,
upper or lower quantile) for the analysis;
- Alternatively, Multivariate Quantile LISA analysis can be used for hotspot
identification. The steps are similar to the bivariable Quantile LISA analysis
shown above.